Scientific inventions done by Indians
India has a rich history of scientific advancements and inventions that date back thousands of years. Early Indian civilization made significant contributions to various fields of science, including mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and metallurgy. Here are some notable early inventions in science by Indians:
Zero (0): One of the most significant contributions of ancient Indian mathematicians was the invention of the concept of zero. The concept of zero as a numerical placeholder was developed in India before the 5th century CE, which revolutionized mathematics and laid the foundation for modern numeral systems. Previously an inscription in Gwalior fort was considered to be oldest known zero, but Radio carbon dating of Bakhshali manuscript has revealed that this manuscript belongs to 2nd to 3rd century CE, making the earliest of surviving documents with zero.
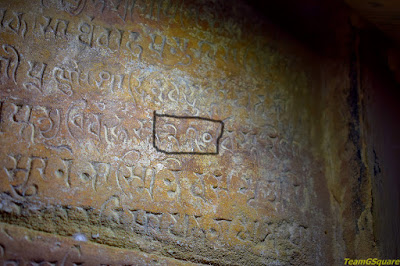 |
| Zero documented at Gwalior Fort |
Decimal System: Indian mathematicians also developed the decimal system, which is the basis for our modern numbering system. They introduced the use of place value notation, including the digit zero, which greatly simplified mathematical calculations and made large numbers more manageable.
Ayurveda: Ayurveda, the traditional Indian system of medicine, is believed to have originated more than 5,000 years ago. It encompasses a holistic approach to healthcare, emphasizing the balance between the body, mind, and spirit. Ayurveda includes various herbal remedies, dietary guidelines, and therapeutic practices that have been used for centuries to treat and prevent ailments.
Yoga: Although primarily a spiritual and philosophical practice, yoga is also considered a science of the mind and body. It originated in ancient India and combines physical postures, breathing exercises, meditation, and ethical principles to promote physical and mental well-being. Yoga has gained widespread recognition and adoption worldwide.
Iron and Steel Production: Ancient Indians were pioneers in iron and steel production. The Iron Pillar of Delhi, dating back to the 4th century CE, stands as a testament to their metallurgical skills. It is a remarkable example of corrosion resistance, which showcases their understanding of iron working techniques.
Astronomy: Indian astronomers made significant contributions to the field of astronomy. The earliest recorded astronomical observations in India date back to the Indus Valley Civilization around 2,500 BCE. Ancient Indian astronomers accurately calculated the duration of a year, the movements of celestial bodies, and developed sophisticated instruments for observation.
Sushruta Samhita: The Sushruta Samhita, written by the ancient Indian surgeon Sushruta, is one of the oldest known texts on surgery. It provides detailed descriptions of various surgical procedures, instruments, and methods of anesthesia. Sushruta's work laid the foundation for many surgical techniques still in use today.
Water Harvesting and Irrigation Systems: Indian civilizations developed advanced systems for water harvesting and irrigation. Techniques such as building step wells, reservoirs, and canals were employed to collect and distribute water for agriculture, providing a sustainable means of cultivation in arid regions.
These are just a few examples of the early inventions in science by Indians. The contributions of ancient Indian scientists and scholars have had a profound impact on various fields of knowledge, and their ideas continue to resonate and inspire modern scientific advancements.


_theatrical_poster_(retouched).jpg)
Comments
Post a Comment